Sharding
Range-based sharding
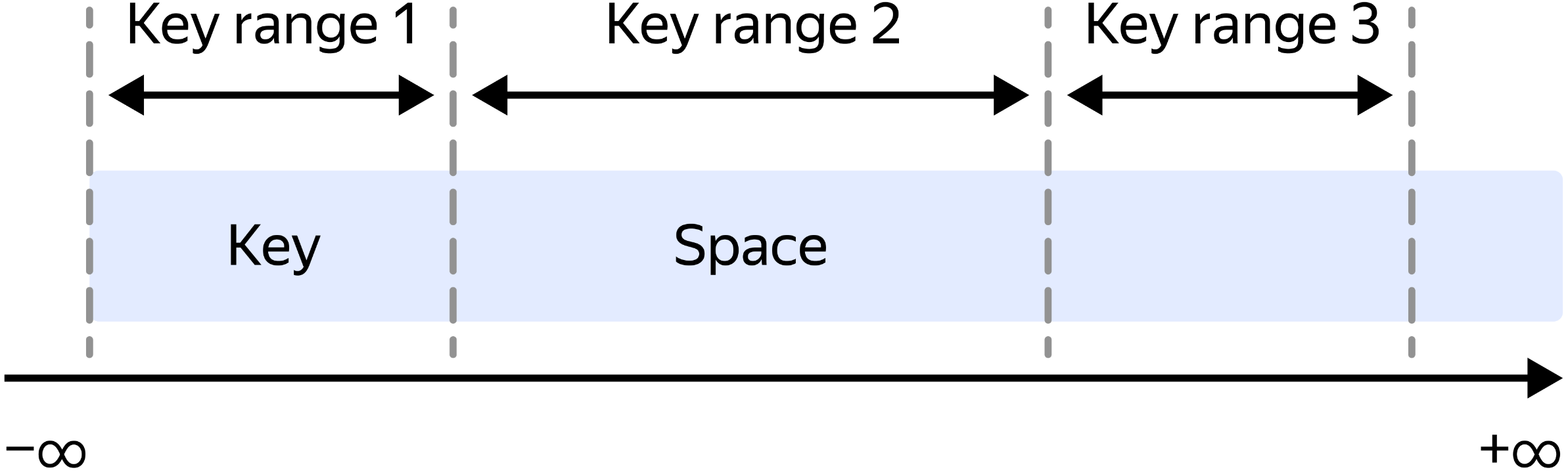
Range-based sharding is a method of distributing data across multiple database shards where each shard holds a contiguous range of data. This is typically done based on a specific key (we call it sharding key), such as a numeric ID, UUID or a date.
For example, if you are sharding a database of user records by user ID, you might have one shard that holds users with IDs from 1 to 1000, another shard that holds users with IDs from 1001 to 2000, and so on.
This method allows for efficient range queries, as all the data within a specific range is located on the same shard. However, it can lead to uneven distribution of data and load between key ranges.
 For clarity, we recommend you take a look get started guide.
For clarity, we recommend you take a look get started guide.

⌘I